Infrastructure Internal and External Audit
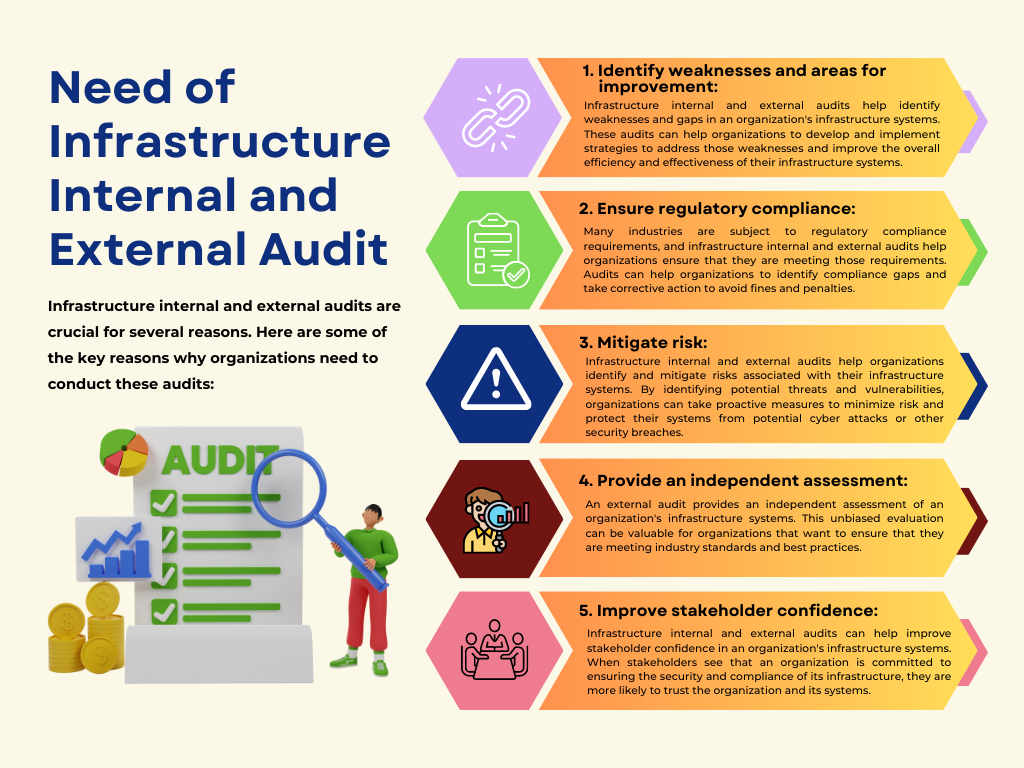
Infrastructure internal and external audits are critical processes that organizations undertake to ensure that their infrastructure systems are operating as intended, secure, and compliant with relevant laws and regulations.
An internal audit is conducted by the organization's internal audit team to assess the adequacy of internal controls, processes, and systems. The team typically consists of employees within the organization who are independent of the system or process being audited. The internal audit team conducts regular assessments of the infrastructure system to identify areas of improvement and provide recommendations to the organization's management.
On the other hand, an external audit is conducted by an independent third-party auditor who evaluates the organization's infrastructure system's controls, processes, and systems. The auditor examines the infrastructure system to ensure that it complies with industry standards, regulations, and best practices. The external audit typically involves a comprehensive review of the infrastructure system, including security, compliance, and overall performance.
Both internal and external audits are important for organizations to maintain the integrity and security of their infrastructure systems. The internal audit team ensures that internal controls are effective and identify areas of improvement, while external auditors provide an unbiased assessment of the organization's compliance with regulations and industry standards.
Methods of Infrastructure Internal and External Audit
There are different methods that organizations can use for infrastructure internal and external audits. Here are some common methods:
Review of documentation: This method involves reviewing documentation such as policies, procedures, and controls to assess the adequacy of the organization's infrastructure system. This is often done during an internal audit.
Interviews: Interviews with key personnel involved in the organization's infrastructure system can help an auditor gain insights into the effectiveness of the system. This method can be used in both internal and external audits.
Observation: Observation involves physically examining the organization's infrastructure system to identify weaknesses and gaps. This method is often used in external audits.
Testing: Testing involves performing a series of tests to assess the effectiveness of the organization's infrastructure system. This method is often used in both internal and external audits.
Sampling: Sampling involves taking a representative sample of transactions or data to assess the adequacy of controls and identify any exceptions. This method is often used in both internal and external audits.
Automated tools: Automated tools such as vulnerability scanners and intrusion detection systems can help identify vulnerabilities in an organization's infrastructure system. These tools are often used in external audits.
Tools used in Infrastructure Internal and External Audit
Infrastructure internal and external audits involve using various tools and technologies to assess the adequacy and effectiveness of an organization's infrastructure system. Here are some common tools used in infrastructure internal and external audits:
- Vulnerability scanners: Vulnerability scanners are automated tools that help identify vulnerabilities in an organization's infrastructure system. These tools scan the system for potential vulnerabilities such as outdated software, missing security patches, or misconfigured settings.
- Intrusion detection systems: Intrusion detection systems (IDS) monitor network traffic and identify potential security threats. These tools can alert organizations to potential security breaches and help them respond quickly to minimize damage.
- Penetration testing tools: Penetration testing tools are used to simulate cyber attacks to test the effectiveness of an organization's security controls. These tools can help organizations identify vulnerabilities and implement measures to mitigate them.
- Configuration management tools: Configuration management tools help organizations manage and track changes to their infrastructure systems. These tools can help ensure that the system is configured correctly and that changes are made in a controlled and documented manner.
- Audit management software: Audit management software can help organizations manage the audit process, from planning and scheduling to reporting and follow-up. These tools can help ensure that audits are conducted efficiently and effectively.
- Compliance management software: Compliance management software helps organizations manage compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards. These tools can help organizations track compliance tasks, monitor progress, and generate compliance reports.
In conclusion, there are several tools available to organizations for infrastructure internal and external audits. These tools can help identify vulnerabilities, monitor for potential security threats, simulate cyber-attacks, manage and track changes to infrastructure systems, and manage compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards.
GET STARTED
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)


.png)